Methods to analyze and evaluate welding seams
Applied Standards
- VT ISO17637
- PT ISO3452
- RT EN16016
Our methods, an overview:
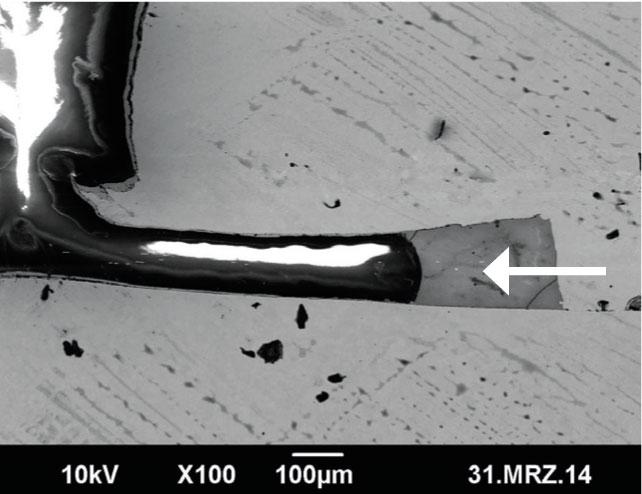
- Visual inspection to ascertain flaws in the exterior appearance of the welding seam
- Metallographic analysis methods to unveil the metals’ inner structure as well as their alloys
- XRF and SEM/EDX analyses to ascertain the chemical composition of the welding seam
- Analyzing the welding seam’s hardness progression using nanoindentation together with a microsection
- 2D/3D x-ray inspection to ascertain irregularities inside the welding seam
Welding seams have to fulfil certain quality criteria or features for components to be bonded together in a way that satisfies their required and expected lifespan.
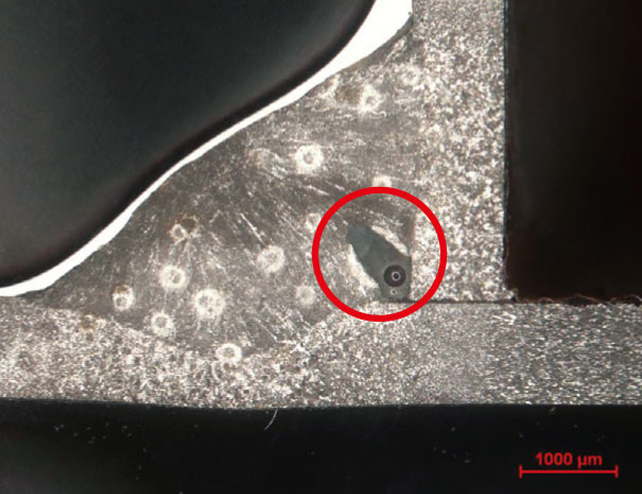
HTV analyzes and evaluates welding seams using several methods and processes (both invasive and non-invasive) to unveil flaws such as fractures, voids, flawed bondings, inclusions or pores or anything else that might negatively affect a welding seam’s hardness.
A welding seam’s exterior apperance can be evaluated with a detailed light microscopic inspection to non-invasively ascertain and document all kinds of visible surface flaws such as fractures, voids, pores, corrosion etc.
Metallographic analysis methods such as microsectioning as well as enhanced microstructure preparation (chemical and/or physical decoration techniques) unveil grain structures even in the micrometer range. Following this up with a high-precision analysis using microscopy or XRF and SEM/EDX analyses definitively identifies flaws such as those in the seam structure or inside the formation of the thermal influence area.
A welding seam’s hardness progression is analyzed using an instrumented intrusion test (nanoindentation) resulting in a location accurate analysis of the base material, the thermal influence area as well as the actual welding seam in the cross section of the microsection sample.
HTV ensures a comprehensive and reliable quality control of welding seams using multiple additional methods such as the 2D/3D x-ray inspection which is specifically useful to identify voids and bonding flaws.